Honing Associated Technologies: Enhancing Precision in Cylinder Machining
- Nagel do Brasil

- Jun 12, 2024
- 2 min read
In the realm of mechanical engineering, honing stands as a crucial practice for refining the precision and quality of components. However, to achieve exceptional outcomes, a thorough understanding and utilization of associated technologies are paramount. Let's delve into some of these technologies and their impact on cylinder machining.
Essential Technologies Associated with Honing
Tecnologias essenciais associadas ao brunimento.
Influência do cross hatch angle na vedação.
Precisão proporcionada pelas réguas diamantadas.
Benefícios do CBN e Borazon como abrasivos.
Etapa crucial do platô no brunimento.
Cross Hatch Angle

This fundamental element in cylinder honing dictates the direction and depth of grooves on the honed surface, directly influencing sealing effectiveness and wear reduction over time. Precise control of the cross hatch angle is essential to ensure the functionality and durability of cylinders.
Abrasives

Abrasives serve a fundamental role in the honing process, responsible for controlled material removal and achieving the desired cylinder surface finish. They vary in composition and hardness, depending on the application's demands. The appropriate selection of abrasives is critical to guarantee high-quality machining results.
Diamond Hone
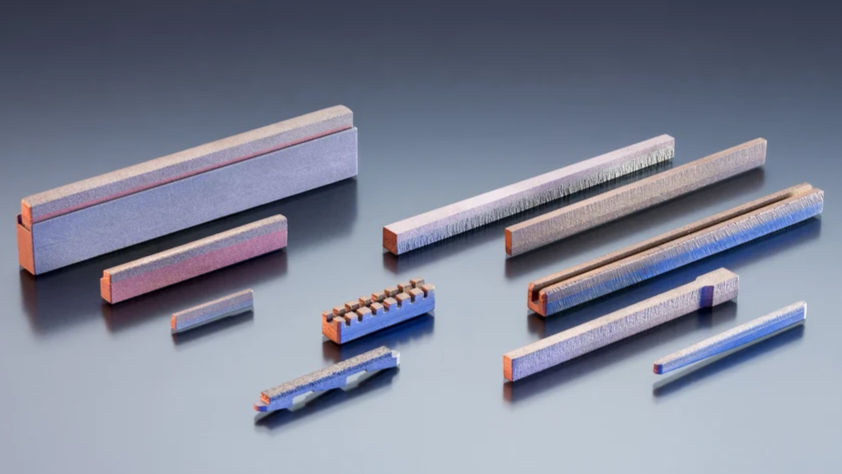
Diamond hones play a pivotal role in the honing process, delivering superior finish and precision. They ensure uniform material removal and achieve the desired surface texture. These abrasive tools are indispensable for attaining high-quality results in cylinder machining.
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride)
CBN, a high-performance abrasive, finds extensive use in cylinder honing. Its exceptional hardness and wear resistance make it ideal for working with metallic materials, yielding precise and efficient machining outcomes. The utilization of CBN significantly contributes to achieving high-quality surfaces and dimensional accuracy.
Plateauing
Plateau honing is mainly used in the cylinder liners of internal combustion engines and is the result of two honing operations.
The first operation, known as base honing, uses a coarse diamond grit to create deep grooves that must be present on the surface profile.
In the second operation, called plateau honing, material removal is minimal, practically not altering the piece's dimensions. Its main goal is to remove the peaks of the profile produced by the base honing operation.
The objective of plateau honing is to develop a specific structure, which presents a periodic profile with large flat areas separated by grooves.
The profile generated in this process differs from the one obtained through finish honing, mainly due to better wear resistance characteristics and oil retention.
Get in touch and explore how our technologies can be tailored to your needs





Comments